Adnomination is a rhetorical device that involves the use of words with similar sounds but different meanings, often to create emphasis or a rhythmic quality in writing. It is frequently used in poetry to add a musical element to the language, engaging readers through repetition and sound.
Further, I explain definition of adnomination, its various types, its effects on the reader, and its use in literature and poetry to enhance meaning and rhythm. Then I examine how this technique creates memorable and emotionally resonant experiences for the audience.
What is The Literary Definition of Adnomination?
Adnomination is a rhetorical device in which the author uses words that are similar in sound but different in meaning, often to create emphasis or a particular effect. This technique is primarily used to intensify the meaning of a phrase or a sentence, enhancing the auditory experience in the reader or listener’s mind.
Example: “She sells sea shells by the sea shore.” The repetition of the “s” sound emphasizes the idea and creates a rhythmic flow.
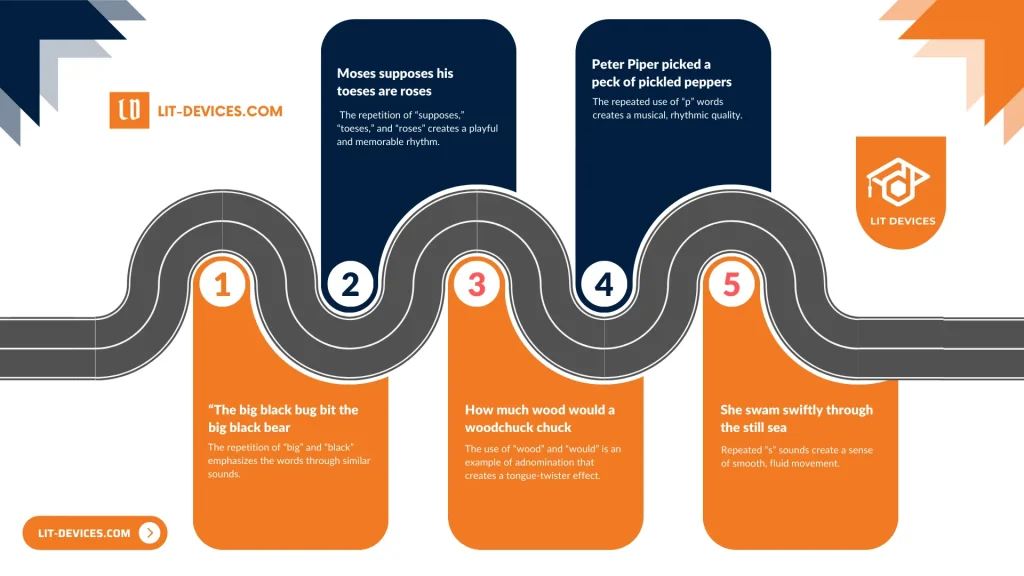
What Are the 5 Examples for Adnomination?
Here are five examples of adnomination in literature and poetry:
- “The big black bug bit the big black bear” – The repetition of “big” and “black” emphasizes the words through similar sounds.
- “Moses supposes his toeses are roses” – The repetition of “supposes,” “toeses,” and “roses” creates a playful and memorable rhythm.
- “How much wood would a woodchuck chuck” – The use of “wood” and “would” is an example of adnomination that creates a tongue-twister effect.
- “Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers” – The repeated use of “p” words creates a musical, rhythmic quality.
- “She swam swiftly through the still sea” – Repeated “s” sounds create a sense of smooth, fluid movement.
What Are the Synonyms & Antonyms in Adnomination?
| Synonyms | Antonyms |
|---|---|
| Alliteration | Dispersal |
| Assonance | Silence |
| Consonance | Monotony |
| Repetition | Novelty |
| Echo | Uniqueness |
Where Does the “Adnomination” Come From?
The term adnomination comes from the Latin word adnominatio, which means “to name in addition.” It refers to the repetition of words with similar sounds, often used in poetry, rhetoric, and literary works. The device has been used since ancient times, particularly in classical poetry and literature, to add a musical quality to language and evoke emotional responses from the audience.
What Are the Types of Adnomination?
There are two main types of adnomination:
- Phonetic Adnomination – This refers to the repetition of similar sounds in adjacent words. This is the most common form of adnomination, often found in tongue twisters and poetry.
- Example: “The silly song sang on.”
- Morphological Adnomination – This type involves the repetition of words derived from the same root but with different meanings or forms.
- Example: “The poet’s poise was poetry in motion.”
Why Writers Use Adnomination?
Writers use adnomination, especially in poetry, to enhance the auditory qualities of their work. It creates rhythm, reinforces meaning, and often helps to emphasize key themes or concepts. The repetitive sounds help readers connect more deeply with the content and can make the writing more memorable. Adnomination also helps create a flow that supports the emotional tone or mood of the piece.
How Adnomination Effects the Reader?
Adnomination affects the reader by creating a musicality and rhythm in the text. This technique helps engage the reader’s auditory senses, making the experience of reading more immersive. Studies have shown that repetitive sounds, like those found in adnomination, help improve memory retention and can intensify the emotional impact of the words.

