Allusion is a literary device that makes indirect references to well-known people, events, places, or works of art to enrich the meaning of a text. By invoking shared knowledge, allusions help readers draw connections and deepen their understanding of the subject matter. This article explores the definition, types, examples, and techniques for using allusion effectively in writing, along with its role in enhancing literature and engaging readers.
What is The Definition of Allusion?
Allusion is a literary device where a writer refers to a well-known person, event, place, or work of art, either directly or indirectly, without explicitly mentioning it.
In Shakespeare’s “Hamlet,” the phrase “It’s all Greek to me” alludes to the difficulty of understanding something, referencing ancient Greek language and culture.
According to a study published by The University of Chicago Press, allusions in literature are used to deepen a reader’s understanding and engagement by drawing on their familiarity with cultural, historical, or literary references.
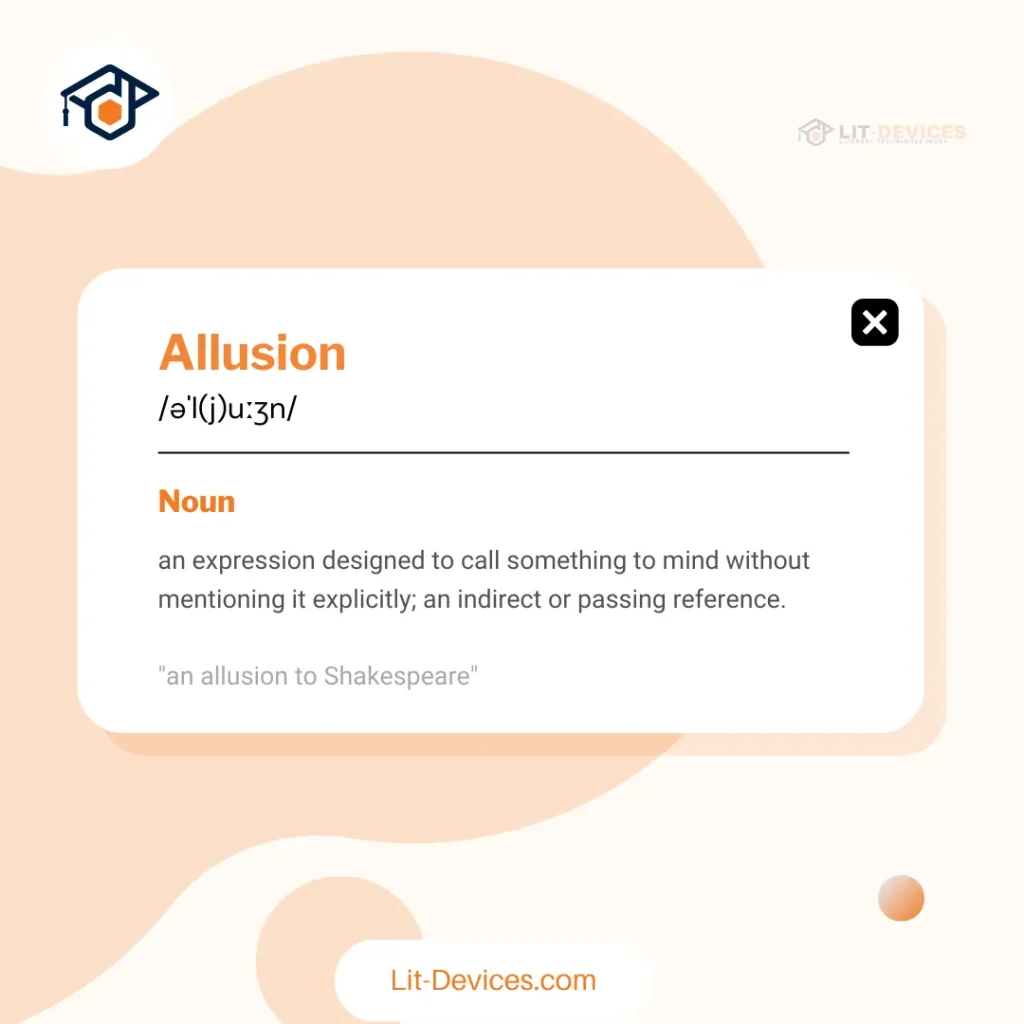
How You Describe Allusion in Simple Terms?
Allusion is a way to make a reference to something familiar, like a famous person, place, or event, without directly stating it. It is often used to give a deeper meaning or context by connecting the text to well-known ideas or themes.
What are the Examples for Allusion?
- In a Poem:
In John Keats’ “Ode on a Grecian Urn”, the reference to ancient Greek culture is an allusion. Keats uses the urn, a Greek artifact, to explore timeless beauty and the fleeting nature of human life.- “Thou still unravish’d bride of quietness,
Thou foster-child of Silence and slow Time.” (Keats, “Ode on a Grecian Urn”)
- “Thou still unravish’d bride of quietness,
- In Literature:
In Moby Dick by Herman Melville, the character Ishmael alludes to the Biblical story of Jonah and the whale, drawing parallels to the themes of fate and struggle.- “Call me Ishmael.” (Melville, Moby Dick) is an allusion to the Biblical story of Jonah who was swallowed by a whale.
- In Movies:
In The Matrix, Neo’s journey alludes to the story of “The One,” a messianic figure, a reference to religious texts like the Bible.- The character Neo is frequently compared to a Christ-like figure in popular culture.
What are the Synonyms & Antonyms?
| Synonyms | Antonyms |
|---|---|
| Reference | Misinterpretation |
| Mention | Obscurity |
| Allude | Disregard |
| Hint | Neglect |
| Indirect reference | Direct statement |
Where Did the Word “Allusion” Come From?
The word “allusion” originates from the Latin alludere, meaning “to play with” or “to refer to indirectly.” It entered the English language around the late 16th century. The use of allusion in literature began to grow in popularity during the Renaissance and has remained a significant stylistic tool in literary works since then. According to a study by The Oxford English Dictionary, the term was first documented in 1580 and became increasingly common in literary and poetic works from the 18th century onward.
What are the Types of Allusion?
Allusions can be categorized into different types based on the reference they make, such as literary, historical, religious, or cultural. Each type uses a well-known concept or figure to help deepen the meaning of the text and create connections with the reader’s prior knowledge.
- Literary Allusion:
Literary allusion refers to references made to well-known works of literature, characters, or events.
Example: In The Great Gatsby, the character Daisy is an allusion to the idealized figure of the “American Dream,” drawing connections to American literature and ideals. - Historical Allusion:
This type involves referencing historical events or figures to enhance the narrative.
Example: In Animal Farm by George Orwell, the reference to Napoleon alludes to Napoleon Bonaparte, using his name to represent a dictatorial leader. - Religious Allusion:
Religious allusion makes reference to religious figures, stories, or themes to express deeper meanings.
Example: In The Grapes of Wrath by John Steinbeck, the character Tom Joad is compared to the Biblical figure of Moses, symbolizing leadership and deliverance. - Cultural Allusion:
A cultural allusion involves referencing aspects of society, such as customs, traditions, or popular culture.
Example: In the movie The Matrix, Neo is an allusion to the archetype of the “Chosen One,” a common theme in global cultures and myths.
How to Use Allusion in Writing?
To use allusion in writing, incorporate references to well-known figures, events, or works that are relevant to the theme of your text. Ensure that your audience has enough background knowledge to recognize and understand these references, which will deepen their engagement with your message. Use allusions sparingly to avoid confusion or overcomplication.
What Are the Best Techniques for Using Allusion?
Allusion can be a powerful tool in writing when used effectively. Here are the best techniques to incorporate allusions in your work:
- Contextual Placement:
Place the allusion in a context where it aligns with the message or theme you are conveying. - Subtlety:
Use allusions that are subtle but still impactful, allowing readers to draw connections without over-explaining. - Relatability:
Choose references that are familiar to your target audience to ensure they can understand and appreciate the allusion. - Integrating Multiple References:
Combine several allusions from different categories (literary, historical, etc.) to enrich the depth of your writing. - Clear Connection:
Make sure the allusion clearly connects to the main theme or idea of your text for coherence and relevance.
What is Allusion, Is It When You Compare Something?
Allusion is not exactly a comparison; rather, it is a reference to a well-known person, event, or work of art. While comparisons (like metaphors or similes) draw direct similarities between things, allusion simply hints at or refers to something external without explicitly stating it. It uses the reader’s familiarity with that reference to add depth or meaning.

