Diction is the deliberate choice and use of words in writing, which shapes the tone, style, and meaning of a text. It plays a crucial role in literature, poetry, song lyrics, and everyday communication, influencing how a message is perceived by the reader.
The types of diction include formal, informal, colloquial, slang, and abstract, each serving different functions and evoking varied emotional responses. Writers use diction to engage their audience, set the tone, and enhance clarity, with specific techniques employed to match the purpose and context of the writing.
Understanding the difference between diction and syntax, as well as identifying diction through word choice, helps readers grasp a writer’s intent and the underlying themes of a work.
What is The Literary Definition of Diction?
Diction is the choice and use of words and phrases in writing. It reflects the writer’s style and influences the tone and clarity of the work. For example, in formal writing, a writer may choose precise, academic vocabulary, while in casual writing, the language may be more conversational and relaxed.
How You Describe Diction in Simple Terms?
Diction refers to the words an author selects to convey meaning, tone, and mood. In simple terms, it’s the way a writer chooses words to express ideas. For instance, a writer may use informal words like “kids” instead of the formal “children” to create a more relaxed tone. A study by the University of California, Berkeley, highlights how diction can impact reader engagement, with more approachable language leading to higher reader connection in certain contexts.
What Are the 5 Examples for Diction?
Diction can be found in various literary forms, including song lyrics, poetry, music, and movies. Below are five examples:
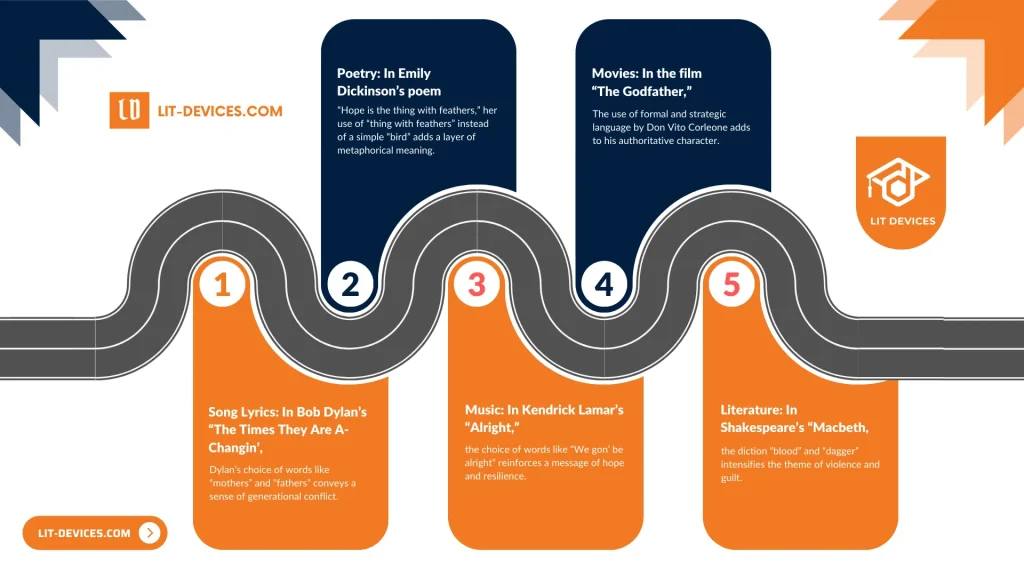
- Song Lyrics: In Bob Dylan’s “The Times They Are A-Changin’,” Dylan’s choice of words like “mothers” and “fathers” conveys a sense of generational conflict.
- Poetry: In Emily Dickinson’s poem “Hope is the thing with feathers,” her use of “thing with feathers” instead of a simple “bird” adds a layer of metaphorical meaning.
- Music: In Kendrick Lamar’s “Alright,” the choice of words like “We gon’ be alright” reinforces a message of hope and resilience.
- Movies: In the film “The Godfather,” the use of formal and strategic language by Don Vito Corleone adds to his authoritative character.
- Literature: In Shakespeare’s “Macbeth,” the diction “blood” and “dagger” intensifies the theme of violence and guilt.
What Are the Synonyms & Antonyms of Diction?
Here are the synonyms and antonyms of diction:
| Synonyms | Antonyms |
|---|---|
| Vocabulary | Ambiguity |
| Language | Vagueness |
| Expression | Indistinctness |
| Terminology | Muddiness |
| Phraseology | Uncertainty |
Where Does “Diction” Come From?
The word “diction” originates from the Latin word dictio, which means “a saying, speech, or style of speaking.” It evolved into the English language during the 16th century. The Oxford English Dictionary traces its first use in English to around 1550.
What Are the Types of Diction?
Diction can vary depending on the writer’s intent, the audience, and the form of writing. Types of diction can include formal, informal, colloquial, slang, and abstract diction. These types create different tones and influence how the message is perceived.
- Formal Diction: Used in academic or professional writing, with precise, sophisticated vocabulary. Example: “The committee is hereby authorized to proceed.”
- Informal Diction: Common in everyday conversation, using simpler, more casual language. Example: “Let’s grab a coffee sometime.”
- Colloquial Diction: The use of regional or local language, often informal. Example: “Y’all” in Southern American English.
- Slang Diction: Involves words and expressions not considered formal or standard, often used by a particular group. Example: “Cool” for “good.”
- Abstract Diction: Refers to words that represent ideas or concepts rather than physical objects. Example: “Freedom,” “love,” or “justice.”
Why Writers Use Diction?
Writers use diction to create a specific tone and convey meaning effectively. The choice of words can impact how the reader understands the message and can help establish mood, characterization, and setting. The use of particular diction results in a cause and effect relationship: the cause is the writer’s choice of words, and the effect is the reader’s interpretation and emotional response. Benefits include enhancing clarity, ensuring precision, and evoking particular emotional reactions.
What Are the Best Techniques to Use Diction in Writing?
To use diction effectively in writing, consider the following techniques:
- Know Your Audience: Select words that will resonate with the intended reader, whether formal or informal.
- Match Diction to Purpose: Choose words that fit the purpose of the writing, whether it’s to inform, entertain, or persuade.
- Tone Consistency: Maintain a consistent tone by aligning the word choice throughout the piece.
- Function of Diction: Understand the role that diction plays in creating atmosphere, reflecting character, and shaping theme.
What Is the Difference Between Diction and Syntax?
Diction refers to the choice of words, while syntax refers to the arrangement of those words in sentences. Both are crucial to the style of writing but focus on different elements.
| Diction | Syntax |
|---|---|
| Involves word choice | Involves sentence structure |
| Affects tone, mood, and meaning of words | Affects flow, clarity, and readability |
| Influences character development and themes | Shapes how ideas are communicated |
How to Identify Diction?
To identify diction in a text, pay attention to the writer’s word choices and the context in which they are used. Diction can be recognized by looking for words that convey a specific tone, mood, or style, which may reflect the character, setting, or theme. A study by the University of Toronto explains that analyzing diction helps readers understand a writer’s voice and intent (University of Toronto, 2021). Identifying diction involves noting the formality or informality, precision, or emotional weight of the words used.

