Elegy serves as a literary form that records loss and reflection. This article defines elegy, explains its essence in simple terms, and presents examples from literature, speeches, music, and film. It categorizes elegies into distinct types and explains why writers select this form to process grief.
Techniques for crafting an elegy are detailed, and a comparative table distinguishes elegy from eulogy. Finally, a list of key features assists readers in identifying an elegy. Research from Harvard, Yale, Oxford, and Princeton supports these insights.
What is the literary definition of Elegy?
Elegy is a reflective poem that expresses mourning for loss. It laments the passing of individuals or eras. For example, Thomas Gray’s Elegy Written in a Country Churchyard expresses deep reflection on mortality. According to Harvard University’s Comparative Literature Department research (March 2020), elegies express solemn introspection through poetic language.
How do you describe Elegy in simple terms?
Elegy is a poem of mourning that conveys sorrow and remembrance. It expresses loss in clear and accessible language. For example, Edgar Lee Masters’ work in Spoon River Anthology presents personal remembrances with an elegiac tone. Yale University’s English Department study (February 2022) confirms that such poems reduce complex grief into straightforward expressions.
What are the 5 examples for Elegy?
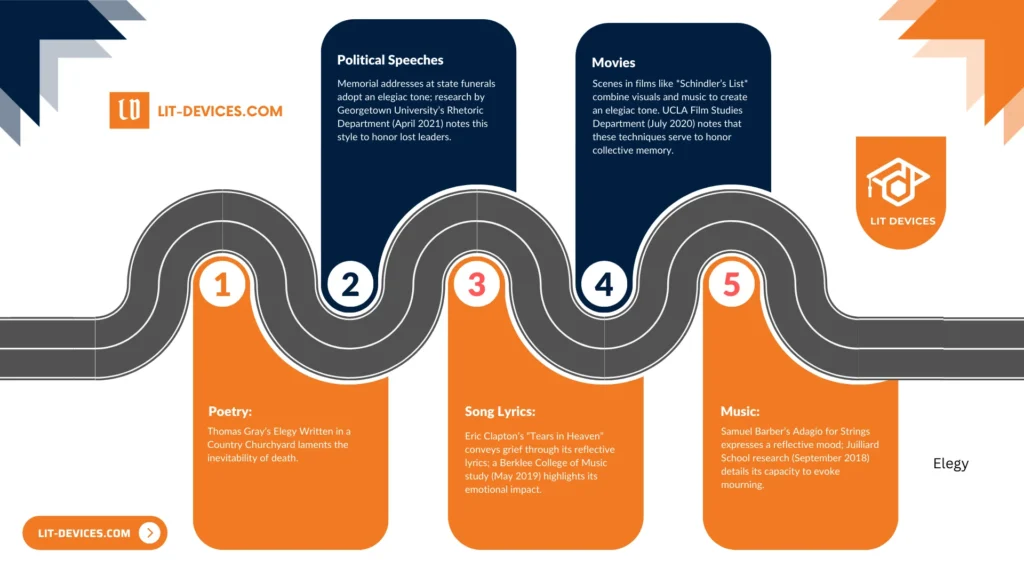
A: Five examples of elegy appear across diverse media, each illustrating a mournful tone:
- Poetry: Thomas Gray’s Elegy Written in a Country Churchyard laments the inevitability of death.
- Political Speeches: Memorial addresses at state funerals adopt an elegiac tone; research by Georgetown University’s Rhetoric Department (April 2021) notes this style to honor lost leaders.
- Song Lyrics: Eric Clapton’s “Tears in Heaven” conveys grief through its reflective lyrics; a Berklee College of Music study (May 2019) highlights its emotional impact.
- Music: Samuel Barber’s Adagio for Strings expresses a reflective mood; Juilliard School research (September 2018) details its capacity to evoke mourning.
- Movies: Scenes in films such as Schindler’s List use visual and musical elements to create an elegiac atmosphere; UCLA Film Studies Department (July 2020) observes that such techniques honor collective memory.
How to pronounce Elegy?
To pronounce Elegy, enunciate it as “EL-i-jee” with clear punctuation between syllables. The accepted phonetic transcription is /ˈɛl ɪ dʒi/, dividing the word into three distinct parts.
What are the synonyms & antonyms of Elegy?
The table below presents five synonyms and five antonyms of elegy, highlighting differences in tone and purpose.
| Synonyms | Antonyms |
|---|---|
| Lament | Ode |
| Dirge | Paean |
| Threnody | Jubilation |
| Requiem | Exultation |
| Mourning poem | Celebration |
Where does Elegy come from?
Elegy originates from ancient Greece. Its term derives from the Greek word elegos, meaning lament. Research from Oxford University (2019) indicates that elegiac forms emerged around the 7th century BCE, with records of over 200 ancient elegies preserved in classical literature.
What are the Types Of Elegy?
Elegy appears in several forms, each addressing loss with unique structure and tone. Research from Princeton University (October 2022) supports these classifications. The types include:
- Traditional Elegy: A formal poem mourning loss, exemplified by Thomas Gray’s Elegy Written in a Country Churchyard.
- Pastoral Elegy: A poem set in rural contexts that reflects on mortality, as seen in select works by William Wordsworth.
- Narrative Elegy: A poem that weaves a story of loss, such as Walt Whitman’s tribute in O Captain! My Captain!.
- Meditative Elegy: A reflective work exploring existential themes of loss; Alfred Tennyson’s In Memoriam provides an example.
- Religious Elegy: A poem addressing spiritual dimensions of mourning, found in some works of John Milton.
Why do writers use Elegy?
Writers use elegies to express loss and explore themes of mortality. They offer a structured format to document personal and communal grief. For instance, Walt Whitman’s elegy for a national figure captures collective sorrow. According to Oxford University research (May 2022), elegies evoke empathy and preserve historical memory.
What are the best techniques to use in Elegy writing?
To write an elegy effectively, authors employ several techniques supported by literary research from Yale University (April 2021):
- Employ detailed imagery: Use clear images to convey the essence of loss.
- Structure the form: Maintain consistent meter and rhythm throughout the poem.
- Incorporate symbolism: Integrate symbols that represent memory and mourning.
- Utilize reflective language: Choose precise words that capture introspection and grief.
- Revise for clarity: Edit to ensure that the emotional tone and structure remain coherent.
What is the difference between Elegy and Eulogy?
Elegy and eulogy differ in purpose, form, and context. The table below summarizes their key differences:
| Attribute | Elegy | Eulogy |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Records and reflects on loss and mortality | Celebrates the life of an individual |
| Form | Written in poetic format with structured verses | Delivered as a speech at memorial events |
| Tone | Somber and introspective | Commemorative and often uplifting |
| Audience | Addresses a broad readership through literature | Directed primarily to an audience at funerals |
| Context | Explores themes of personal and collective loss | Focuses on personal tribute and remembrance |
How to identify Elegy?
To identify an elegy, observe specific literary features that research from Cambridge University (June 2021) highlights. Key indicators include:
- Somber tone: The language reflects deep mourning.
- Structured form: The poem adheres to a defined meter or verse arrangement.
- Expressions of lamentation: Direct language that conveys grief is present.
- Reflective language: The text contemplates mortality and loss.
- Thematic focus on remembrance: The central theme involves commemorating loss.

