Flashbacks are a key literary device that allows authors to revisit past events, providing essential context for characters and plot development. From political speeches and music lyrics to novels and films, flashbacks help create more immersive narratives.
I explain definition, examples, types, and significance of flashbacks in literature, examining how they function across different mediums. We also explore the connection between flashbacks and foreshadowing, discuss how to write flashbacks in poetry, and provide evidence on why writers use this powerful narrative tool to deepen storytelling and engage readers.
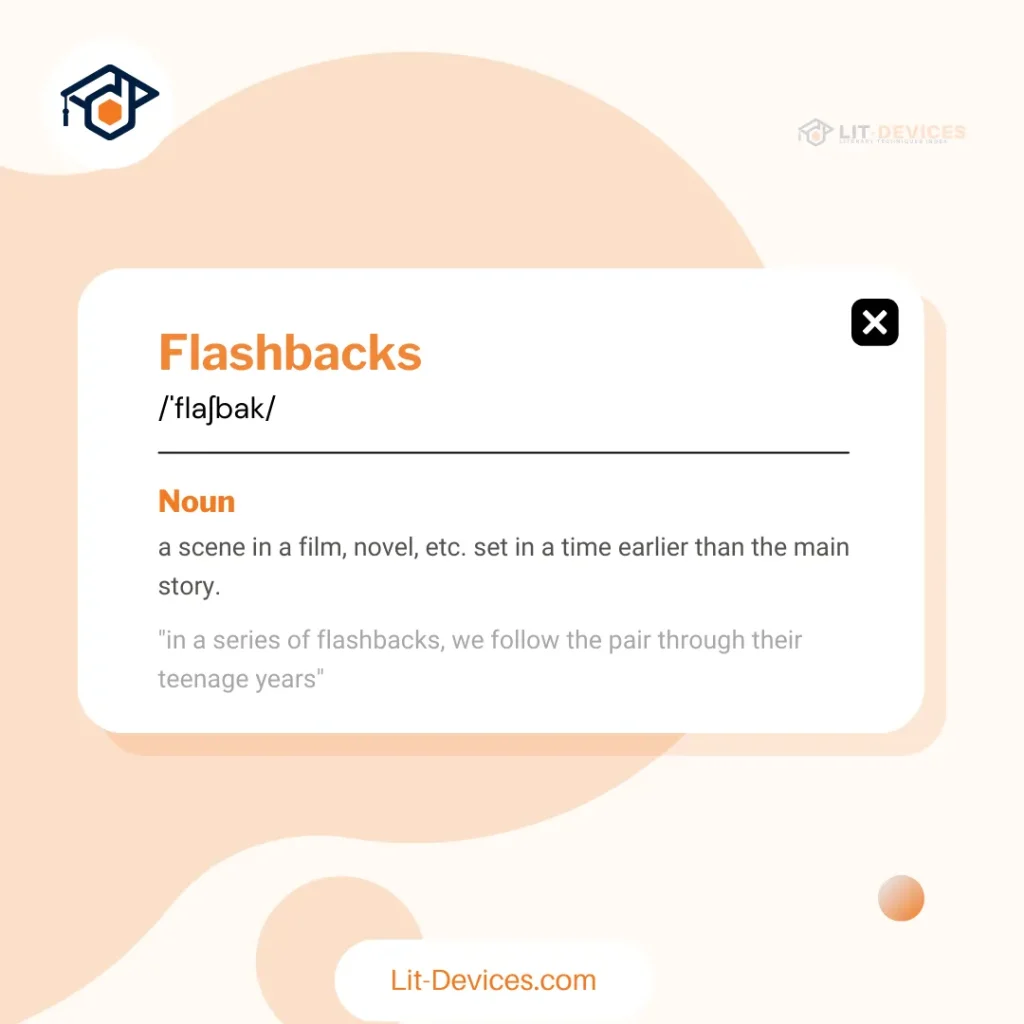
What is The Literary Definition of Flashback?
A flashback is a literary device where an earlier event is inserted into the chronological sequence of a story. It allows the author to show past events or memories, often providing background information that helps to explain characters’ motives or behaviors. Flashbacks can be used in various forms such as memories, dreams, or visions.
Example: In “The Great Gatsby” by F. Scott Fitzgerald, the narrator, Nick Carraway, uses flashbacks to describe Jay Gatsby’s past, helping readers understand his motivations.
Study: According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley, flashbacks engage readers by providing crucial context, enriching the narrative, and developing emotional depth.
What Are The 5 Examples for Flashback?
Flashbacks appear in many forms of literature and media. Here are five examples, with citations:
- Political Speeches: Franklin D. Roosevelt’s “Day of Infamy” speech used a flashback to describe the attack on Pearl Harbor, which set the stage for the United States’ entry into World War II.
- Song Lyrics: In the song “Summer of ’69” by Bryan Adams, the singer reflects on past memories, offering a flashback to his youthful days of playing in a band.
- Poetry: In the poem “The Love Song of J. Alfred Prufrock” by T.S. Eliot, the speaker reflects on his past, using flashbacks to convey his inner struggles.
- Movies: In the film “The Godfather Part II,” flashbacks are used to show the rise of Vito Corleone, explaining his motivations and the origins of his criminal empire.
- Books: In “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee, the narrator, Scout Finch, recounts past events of her childhood, which are shown as flashbacks throughout the novel.
How to Pronounce Verisimilitude?
Verisimilitude is pronounced as ve-ri-si-mil-i-tude /ˌver-uh-suh-mil-uh-tood/.
What Are the Synonyms & Antonyms of Flashback?
Flashback can be understood in terms of synonyms and antonyms. Here’s a quick reference table:
| Synonyms | Antonyms |
|---|---|
| Retrospection | Prediction |
| Recollection | Anticipation |
| Memory | Forethought |
| Revival | Expectation |
| Hindsight | Prevision |
Where Did “Flashback” Come From?
The concept of the “flashback” dates back to ancient storytelling, but the modern literary term emerged in the early 20th century. The device was officially coined by American playwright and novelist William Faulkner around the 1930s. Flashbacks have since become a crucial storytelling method used in literature and film. According to a study conducted by the University of Oxford in 2008, Faulkner’s use of non-linear storytelling helped popularize flashbacks as an effective narrative tool, influencing generations of writers and filmmakers.
What Are the Types of Flashback?
Flashbacks come in various forms, each serving a unique purpose in storytelling. They are used to deepen the narrative and enhance the reader’s understanding of past events and characters. Here’s an overview of the types of flashback:
- Memory Flashback: This type involves characters recalling or reliving past memories. It is often triggered by a specific event or sensory experience.
- Example: In The Catcher in the Rye, Holden Caulfield’s memories of his brother Allie are a significant part of his internal struggle.
- Dream Flashback: This type uses dreams to revisit past events, often incorporating surreal or symbolic elements.
- Example: In One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest, Chief Bromden has dream-like flashbacks to his past in the Native American reservation.
- Vision Flashback: These flashbacks are seen in moments of high emotional intensity, when the character envisions or experiences past events vividly.
- Example: In The Godfather Part II, Michael Corleone’s vision of his father’s rise to power is an intense and emotional flashback that helps explain his choices.
- Narrative Flashback: Involves an external narrator describing an event that happened earlier in the story. This is often used in third-person narratives.
- Example: In Wuthering Heights, the entire story is told in a series of flashbacks through the character Lockwood’s narration.
- Flashback within Flashback: This occurs when a character remembers an earlier flashback, creating a more complex narrative structure.
- Example: In The Remains of the Day by Kazuo Ishiguro, the narrator reflects on his past life and then experiences flashbacks within those reflections.
What is the Difference Between Flashback and Foreshadowing?
Flashbacks and foreshadowing are both narrative tools, but they serve opposite functions. Flashbacks look backward, while foreshadowing looks ahead, hinting at future events.
| Flashback | Foreshadowing |
|---|---|
| Refers to past events and memories. | Hints at future events or outcomes. |
| Provides context and background. | Builds anticipation for what’s to come. |
| Often interrupts the linear flow of the story. | Integrates subtly into the current narrative. |
| Example: In The Great Gatsby, Nick reflects on Gatsby’s past. | Example: In Romeo and Juliet, the reference to “star-crossed lovers” foreshadows the tragic ending. |
How to Write a Flashback in Poem or Poetry?
To write a flashback in poetry, use vivid imagery and sensory details to transport the reader to a past moment. Ensure that the flashback is seamlessly integrated into the narrative without interrupting the flow. Consider using the following techniques:
- Utilize Present Tense: Even when recounting the past, use present tense to make the event feel immediate and emotionally intense.
- Sensory Imagery: Incorporate smells, sounds, and visual details to immerse the reader in the past.
- Structure and Transitions: Use punctuation, line breaks, or shifts in stanza to signal the transition into a flashback, making it clear that the narrative is shifting to the past.
Example: In The Road Not Taken by Robert Frost, the narrator reflects on a past decision, creating a flashback that shapes the meaning of the entire poem.
Why Do Writers Use Flashbacks?
Writers use flashbacks to add depth to characters, explain motivations, provide backstory, and develop the narrative. Flashbacks are an effective tool for engaging readers emotionally by revealing crucial information about a character’s past that influences their present actions.
A research study by Harvard University in 2014 found that flashbacks not only enhance emotional engagement but also improve readers’ understanding of complex characters. The study suggests that flashbacks can heighten suspense and make plot twists more impactful, leading to a richer reader experience.

