Hubris, a central theme in literature, refers to excessive pride or arrogance that ultimately leads to a character’s downfall. This tragic flaw is often seen in characters who overestimate their abilities, ignore authority, or believe they can control forces beyond their understanding.
Writers use hubris to deepen character development, create moral lessons, and add emotional depth to a story. I explain types of hubris, techniques for using it effectively, and how it differs from other literary concepts like foil. It also provides insights on identifying hubris in stories and its significant role in narrative structure.
What is the Literary Definition of Hubris?
Hubris is a form of excessive pride or self-confidence, often leading a character to challenge divine or moral laws. It is typically considered a tragic flaw, as it leads to the character’s downfall or misfortune.
Example: In The Iliad, Achilles displays hubris when he refuses to return to battle out of pride, which leads to his eventual downfall.

How You Describe Hubris in Simple Terms?
Hubris is extreme pride or arrogance that makes someone think they are better or more powerful than they really are. It often leads them to make bad decisions or act recklessly.
Example: In Jurassic Park, John Hammond exhibits hubris by believing he can control nature and create a successful dinosaur theme park, which ends in disaster.
What Are the 5 Examples for Hubris?
Here are five examples of hubris in literature and film:
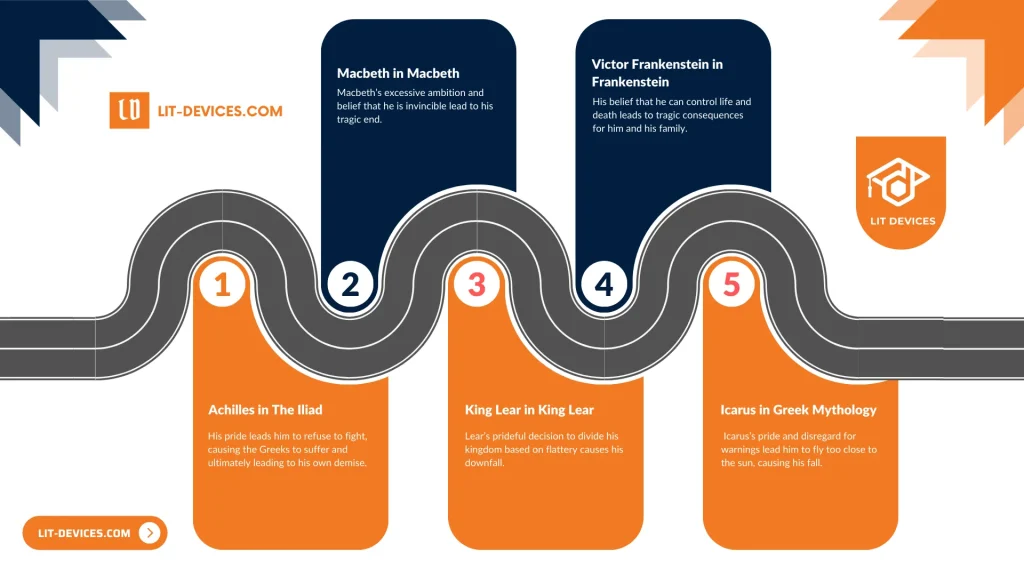
- Achilles in The Iliad – His pride leads him to refuse to fight, causing the Greeks to suffer and ultimately leading to his own demise.
- Macbeth in Macbeth – Macbeth’s excessive ambition and belief that he is invincible lead to his tragic end.
- King Lear in King Lear – Lear’s prideful decision to divide his kingdom based on flattery causes his downfall.
- Victor Frankenstein in Frankenstein – His belief that he can control life and death leads to tragic consequences for him and his family.
- Icarus in Greek Mythology – Icarus’s pride and disregard for warnings lead him to fly too close to the sun, causing his fall.
What Are the Synonyms & Antonyms of Hubris?
| Synonyms | Antonyms |
|---|---|
| Arrogance | Humility |
| Conceit | Modesty |
| Pride | Meekness |
| Self-importance | Selflessness |
| Overconfidence | Caution |
Where Does Hubris Come From?
The concept of hubris originates from ancient Greek literature, particularly in tragedies. In Greek mythology and drama, hubris was seen as a violation of the natural order or divine law, often resulting in punishment from the gods. It was considered one of the most serious faults a hero could possess, as it frequently led to their downfall.
What Are the Types of Hubris?
There are different types of hubris, each exhibiting a unique form of excessive pride or arrogance:
- Overestimating One’s Abilities – Believing one can accomplish anything without limitation.
- Example: Victor Frankenstein in Frankenstein, who believes he can conquer life and death.
- Disrespect for Authority – Ignoring the boundaries set by higher powers, such as gods or moral laws.
- Example: Oedipus in Oedipus Rex, who disregards prophecies and attempts to defy fate.
- Overconfidence in Control – Believing one can control forces beyond their understanding.
- Example: John Hammond in Jurassic Park, who tries to control nature with disastrous results.
- Recklessness – Acting without regard for potential consequences due to an inflated sense of power.
- Example: Icarus, whose reckless flight towards the sun leads to his fall.
- Self-Importance – Treating oneself as being above others or the law.
- Example: King Lear in King Lear, who treats his daughters and kingdom as personal possessions.
Why Writers Use Hubris?
Writers use hubris as a tool to create complex characters and moral lessons. It serves as a tragic flaw, leading to a character’s downfall, which in turn adds depth and drama to a narrative. By using hubris, writers highlight the consequences of excessive pride, illustrating the dangers of overestimating one’s abilities or defying natural or divine laws. It also helps make the story more engaging and allows for the exploration of themes such as human frailty, pride, and the consequences of unchecked ambition.
What Are the Best Techniques to Use Hubris?
Writers can use the following techniques to effectively incorporate hubris into their stories:
- Characterization – Develop a protagonist whose excessive pride or arrogance is apparent through their actions and attitudes.
- Example: In Macbeth, Macbeth’s overconfidence leads to his tragic end.
- Foreshadowing – Hint at the eventual downfall caused by hubris through subtle clues or warnings ignored by the character.
- Example: In Oedipus Rex, the prophecies foreshadow Oedipus’s tragic fate.
- Conflict – Create external conflicts that test the character’s pride and lead to their downfall.
- Example: In The Iliad, Achilles’ pride leads to his refusal to fight, causing a rift in the Greek army.
- Consequences – Illustrate the severe consequences that arise from the character’s hubris.
- Example: In Frankenstein, Victor Frankenstein’s hubris results in the death of his loved ones.
- Dialogue – Use dialogue to emphasize the character’s arrogance, superiority, and disregard for warnings.
What Is the Difference Between Hubris and Foil?
Hubris and foil are distinct literary concepts:
| Aspect | Hubris | Foil |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Excessive pride or arrogance that leads to downfall. | A character who contrasts with another to highlight particular qualities. |
| Purpose | To illustrate a character’s tragic flaw and consequences. | To enhance the characteristics of another character, often the protagonist. |
| Example | Macbeth’s ambition in Macbeth. | Horatio in Hamlet, who contrasts Hamlet’s impulsiveness. |
How to Identify Hubris?
To identify hubris, examine the character’s attitude and behavior. Look for signs of excessive pride, overconfidence, or a disregard for authority. If a character believes they can defy natural or moral laws, or if they ignore warnings and suffer consequences, it is likely an example of hubris. Hubris often manifests in the character’s decisions, actions, and interactions with others, where they believe they are invincible or superior.

