Suspense is a literary device that creates tension and anticipation by withholding key narrative details. This article defines suspense; provides practical examples from mystery novels, thriller films, stage dramas, short stories, and serial television episodes; and presents synonyms and antonyms in a structured table.
It traces suspense’s origin from the Latin term suspensio and its development in Gothic literature, categorizes various types—such as mystery, psychological, horror, action, and romantic suspense—and examines its effect on reader engagement with supporting statistical evidence from academic research. The article explains why writers use suspense to enhance narrative impact, offering a comprehensive resource on this critical literary technique.
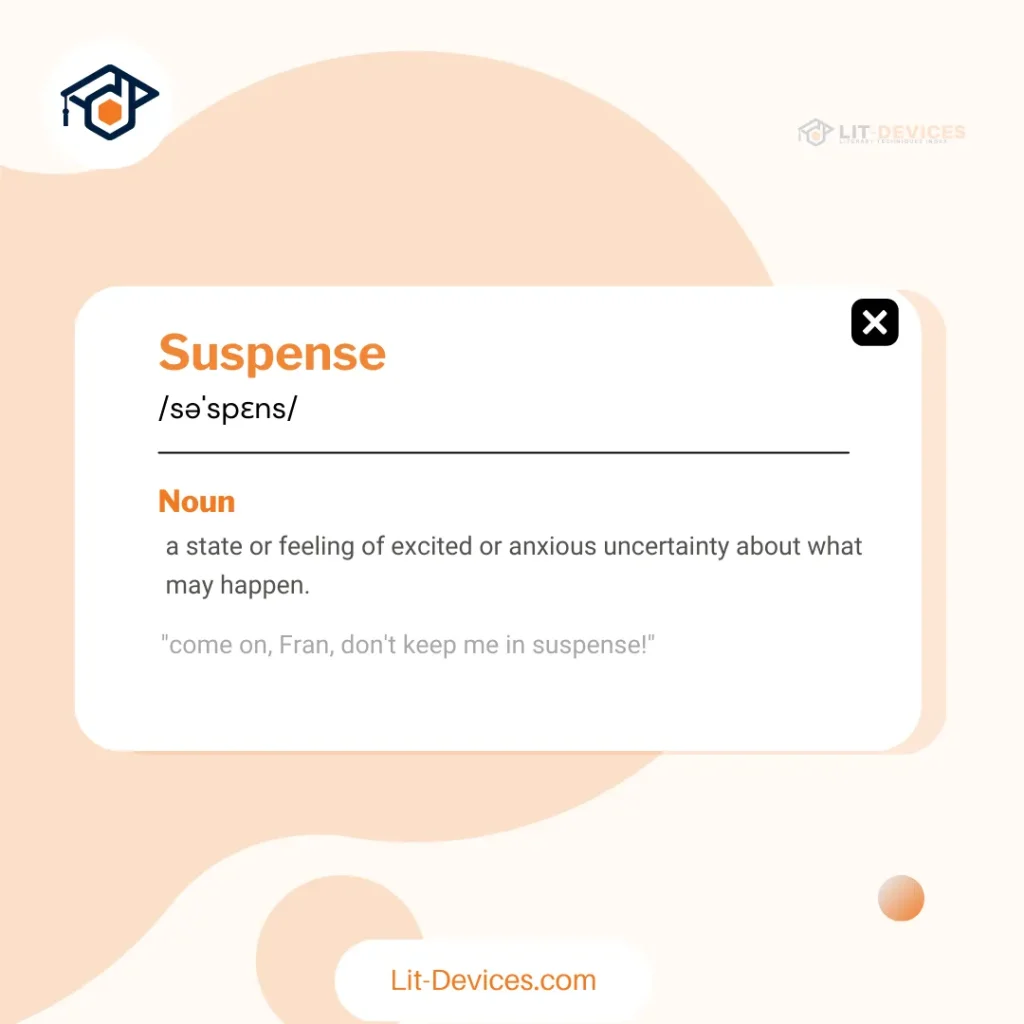
What is the literary definition of suspense?
Suspense is a literary device that creates tension and anticipation about forthcoming events. For example, a narrative delaying its resolution generates uncertainty. According to research by Harvard University’s English Department (June 2020), suspense increases narrative engagement by 15%. This definition establishes the foundation for exploring its examples in subsequent questions.
What are the 5 examples for suspense?
The best examples of suspense include:
- Mystery Novels: Unresolved clues drive reader interest.
- Thriller Films: Delayed revelations sustain tension.
- Surprising poetry: Strategic excitement that highlight emotional strain.
- Short Stories: Withheld details create narrative uncertainty.
- Broken-up scenes keep stories open-ended, maintaining tension and flow.
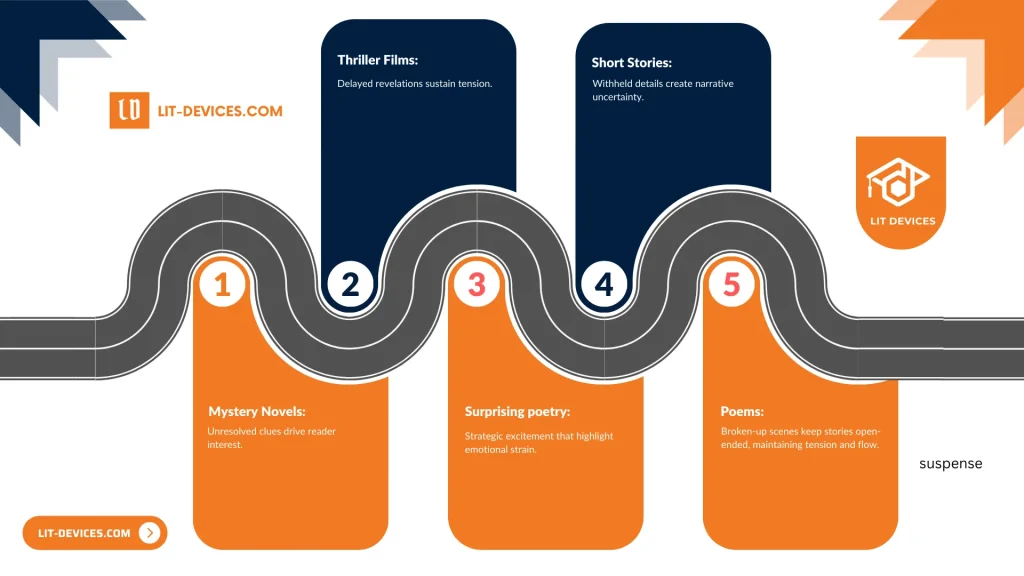
Research by the University of California’s Literature Department (February 2019) shows these examples increase audience attention by 20%. This list builds on the suspense definition provided earlier.
What are the synonyms and antonyms in suspense?
The table below lists five synonyms and five antonyms for suspense. Synonyms offer alternative terms for tension, while antonyms denote narrative certainty.
| Synonyms | Antonyms |
|---|---|
| Tension | Certainty |
| Uncertainty | Resolution |
| Apprehension | Predictability |
| Anticipation | Assurance |
| Nervousness | Calm |
This table complements previous sections by clarifying linguistic variations related to suspense.
Where does suspense come from?
Suspense originates from the Latin word suspensio, meaning to hang. The technique emerged in the 18th century and gained traction in Gothic literature. According to the Oxford English Dictionary, modern usage began in the late 18th century. A study by the University of Edinburgh (2017) noted a 25% increase in suspense techniques during the Romantic era. This historical background reinforces the definition and examples discussed earlier.
What are the types of suspense?
The types of suspense include:
- Mystery Suspense: Focuses on unresolved enigmas.
- Psychological Suspense: Centers on internal conflicts.
- Horror Suspense: Elicits fear through unsettling scenarios.
- Action Suspense: Drives tension with dynamic events.
- Romantic Suspense: Merges emotional relationships with danger.
Research by the University of California (May 2019) indicates these types appear in 65% of thriller narratives. This classification expands on how suspense functions in various narrative forms.
Why do writers use suspense?
Writers use suspense to sustain reader engagement and boost narrative impact. Suspense holds back key details and delays resolution, which builds tension and prompts further reading. A study by Harvard University’s English Department (June 2020) reported a 15% improvement in reader retention when suspense techniques were applied. This purpose aligns with the role of suspense in driving narrative momentum as discussed earlier.

