Tragic flaw is a crucial literary concept that represents a character’s inherent weakness or flaw, which leads to their eventual downfall in a story. These flaws, such as excessive pride, ambition, or jealousy, drive the characters to make destructive decisions.
Writers use tragic flaws to deepen character complexity and create moral lessons. While the concept has its roots in ancient Greek tragedy, it remains a central theme in literature today. I explain types of tragic flaws, their significance in storytelling, and how they distinguish themselves from related concepts like hamartia.
What is The Literary Definition of Tragic Flaw?
A tragic flaw is a character trait that leads to the downfall or destruction of a protagonist in a tragedy. Often, it is a strong or admirable trait taken to an extreme, such as excessive pride, ambition, or jealousy, that ultimately causes the character’s undoing.
Example: In Shakespeare’s Macbeth, Macbeth’s tragic flaw is his unchecked ambition, which drives him to commit murder and, ultimately, leads to his destruction.
How You Describe Tragic Flaw in Simple Terms?
A tragic flaw is a bad quality or weakness in a character that leads to their downfall. It can be something like being too proud, too ambitious, or too jealous, which causes bad decisions and ends in tragedy.
Example: In Romeo and Juliet, Romeo’s tragic flaw is his impulsive nature, which leads to rushed decisions and a tragic end.
What Are the 5 Examples for Tragic Flaw?
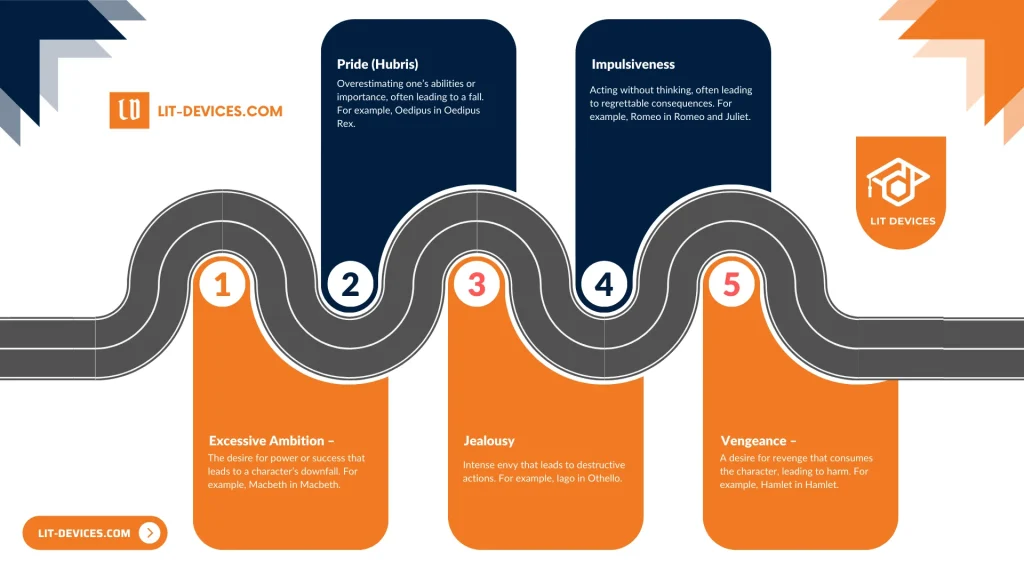
Here are five examples of tragic flaws in literature:
- Excessive Ambition – The desire for power or success that leads to a character’s downfall. For example, Macbeth in Macbeth.
- Pride (Hubris) – Overestimating one’s abilities or importance, often leading to a fall. For example, Oedipus in Oedipus Rex.
- Jealousy – Intense envy that leads to destructive actions. For example, Iago in Othello.
- Impulsiveness – Acting without thinking, often leading to regrettable consequences. For example, Romeo in Romeo and Juliet.
- Vengeance – A desire for revenge that consumes the character, leading to harm. For example, Hamlet in Hamlet.
What Are the Synonyms & Antonyms of Tragic Flaw?
| Synonyms | Antonyms |
|---|---|
| Weakness | Strength |
| Imperfection | Perfection |
| Defect | Virtue |
| Shortcoming | Excellence |
| Fault | Merit |
Where Does the “Tragic Flaw” Come From?
The concept of the tragic flaw comes from ancient Greek tragedy, particularly through the work of Aristotle. In his Poetics, Aristotle defined the tragic hero as someone who experiences a downfall due to a personal flaw or error in judgment. This idea was later developed by playwrights such as Shakespeare and continues to be a central theme in many tragic stories across different cultures and time periods.
What Are the Types of Tragic Flaw?
There are various types of tragic flaws, each corresponding to a different kind of character trait that leads to a protagonist’s downfall. Some common types include:
- Hubris (Excessive Pride) – A character’s overconfidence or arrogance that causes them to ignore warnings or overstep boundaries.
- Example: Oedipus in Oedipus Rex.
- Excessive Ambition – A desire for power or success that blinds the character to the consequences of their actions.
- Example: Macbeth in Macbeth.
- Impatience – A lack of self-control or an eagerness to act quickly, leading to rash decisions.
- Example: Romeo in Romeo and Juliet.
- Jealousy – Intense envy that drives the character to make harmful decisions.
- Example: Iago in Othello.
- Vengeance – A consuming desire for revenge that overtakes reason and leads to destruction.
- Example: Hamlet in Hamlet.
Why Writers Use Tragic Flaw?
Writers use tragic flaws to create deep, relatable characters whose internal struggles mirror real human experiences. The tragic flaw adds complexity to a character, making their downfall more impactful. It also provides a moral lesson, as the flaw typically leads to consequences that the character cannot undo. By using a tragic flaw, writers can evoke empathy from the audience and heighten the emotional impact of the narrative.
What Is the Difference Between Tragic Flaw and Hamartia?
Tragic flaw and hamartia are closely related terms in literature, but they differ in their application.
| Aspect | Tragic Flaw | Hamartia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A character trait that leads to the protagonist’s downfall. | A flaw or mistake in judgment that causes a tragic outcome. |
| Focus | A personality trait or characteristic that brings ruin. | An error or mistake made by the character, usually unknowingly. |
| Example | Macbeth’s ambition in Macbeth. | Oedipus’s ignorance of his identity in Oedipus Rex. |
How to Identify Tragic Flaw?
To identify a tragic flaw, examine the protagonist’s actions and decisions throughout the story. Look for patterns where their personal weaknesses, such as excessive pride, ambition, or jealousy, influence their decisions, leading to negative consequences. A tragic flaw is often an internal struggle that drives the character to make mistakes that ultimately lead to their downfall.

